Sunday night, December 16th, was the evening of the closest approach of Comet 46P/Wirtanen. The comet was close enough and bright enough with an apparent magnitude between 4.0 and 4.5 that you could see it with the naked eye if you had good, dark skies. Thankfully, that’s just what I have living out in rural Missouri, and we also had crystal clear skies. The comet can be seen between the Pleiades Cluster and Taurus through Wednesday, but as the Moon’s phase transitions from 1st Quarter to Waxing Gibbous, dim objects in the sky will be harder and harder to see. Throughout this coming week, the best time to view the comet will actually be in the very early morning after moonset. You can check out more about where to find and when to view the comet at Sky and Telescope, https://www.skyandtelescope.com/astronomy-news/observing-news/comet-46p-wirtanen-and-moon/.
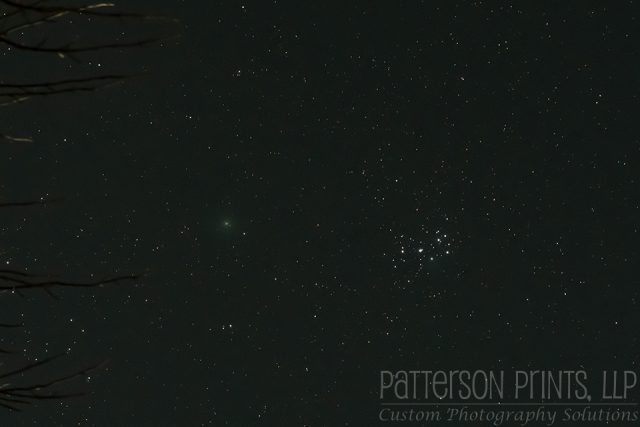

The image below of Comet 46P/Wirtanen is the result of stacking 63 exposures each with a shutter speed of 20-seconds, ISO 6400, aperture f/8, and a focal length of 200 mm on a Nikon D500 through a Tamron 70-200mm f2.8 riding atop a Celestron 8″ SCT. The telescope was there just to provide the clock drive so that the camera moved with the stars’ diurnal motion. Each raw image file was corrected for dark current, bias current, and the response across the frame was normalized using a flat field image. I’ll write up a tutorial on how to collect these images and why they’re necessary later. The images were then aligned and stacked on the comet, which is why the stars appear as streaks. Since the comet is moving quite rapidly past us, its motion relative to the distant background stars is very noticeable, even in the short timespan of this image set.
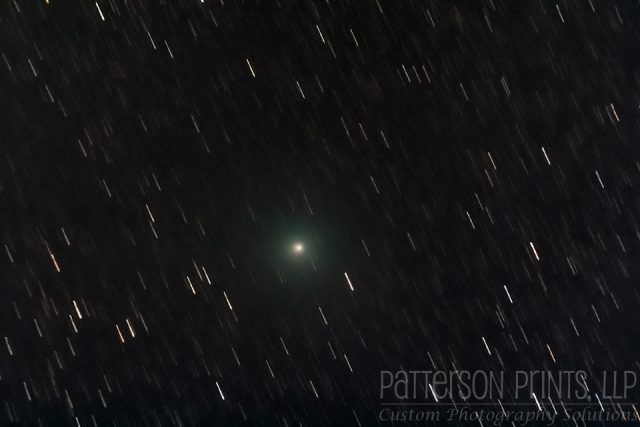

You may have noticed the very green color to many of the images of Comet 46P/Wirtanen, including this one. The green color is not a image processing artifact, but is indicative of the comet’s composition. Most comets contain a enough cyanogen (CN) and diatomic carbon (C2). As a comet approaches the Sun and its surface warms, volatile materials such as cyanogen, water, and others begin to vaporize forming the comet’s coma and tail. When cyanogen and diatomic carbon interact with the Sun’s ultraviolet light and fluoresce to create the characteristic greenish glow of many comets.